Today, the Global e-Sustainability Initiative (GeSI) presents its latest report, ‘Enabling the Global Goals,’ at the third SDG Business Forum in New York. The report is the latest installment in a series stretching back to ten years ago, when GeSI published its first assessment of the potential of information and communication technologies (ICT) in enabling the transition to a low-carbon, sustainable economy.
Over the last decade, we have continuously updated our analysis to reflect the fast evolution of digital technologies; and the adoption of the Sustainable Development Goals by the UN General Assembly provided the world with a new framework to look at sustainable development.
With this in mind, we started exploring the link between digital and the SDGs. First, the GeSI #SystemTransformation report released in 2016 found that digital technologies will be fundamental for the achievement of all 17 SDGs, and over 50% of the 169 related targets.
With Enabling the Global Goals, we take a further step in our analysis and we look at the correlation between digital access and SDG progress. The results are very encouraging: evidence shows that there is a clear, positive link between access and 11 of the 17 SDGs. The strongest correlation is found with the social and economic SDGs: SDG 1 (no poverty), 2 (zero hunger), 3 (good health and well-being), 4 (quality education), 5 (gender equality), 8 (decent work and economic growth), 9 (industry, innovation, and infrastructure), and 16 (peace and justice, strong institutions).
The report also finds early indications of causation: we selected three SDGs for in-depth analysis on health care, gender quality, and climate action, providing a balanced overview of the three areas of impact for the SDGs (people, growth, and the environment). The exploration of the correlation results and the additional analysis we ran on these SDGs shows that the link between digital access and SDG progress is well beyond coincidental.
This is important as it provides us with a solid foundation of data to inform evidence-based decision-making and action. It also helps make better predictions about the quantitative impact of digital access on the SDGs.
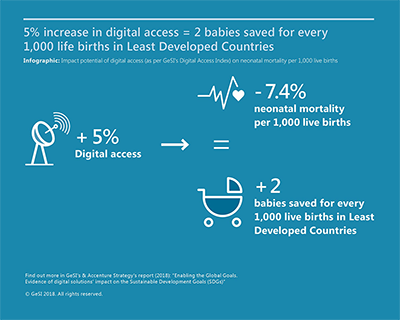
For example, in the case of health care we found that a 5% increase in digital access can result in a decrease in neonatal mortality (defined as occurring in the first 28 days of life) by 7.4%, which translates to two babies saved for every 1,000 live births in Least Developed Countries. For gender equality, the same 5% digital access increase would mean two additional weeks of schooling for girls and women as compared to boys and men, thus contributing to the achievement of the specific SDG 5 indicator on female years of schooling. For environmental SDGs (6, 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15), the picture emerging from the research is somewhat mixed, with the correlation between digital access and those SDGs still unclear (or negative, in the case of SDG 12 on responsible consumption and production).
However, when looking more specifically and closely at climate action, there is reason for optimism: a number of studies, including the SMART series of reports produced by GeSI between 2008 and 2015, clearly show that the application of ICT solutions in sectors such as agriculture, mobility, energy, building and more can enable those sectors to significantly reduce their carbon emissions up to 2030. Indeed, this potential reduction was estimated by previous GeSI research (SMARTer2030 report) at 12.1 gigatons of CO2e to be saved up to 2030, thus helping to hold global emissions at today’s levels and decoupling growth from carbon emissions. In terms of climate action, the further modelling done in our Enabling the Global Goals report shows that a 5% increase in digital access will reduce consumption-based emissions by 1.6%, equivalent to the annual emissions of 468 coal plants.
To track SDG progress, the UN Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN) and the Bertelsmann Foundation have developed an SDG Index, which we have adopted in our analysis. To monitor digital access, however, we also decided to develop a new tool: the GeSI Digital Access Index is focused solely on digital and technology indicators, and it covers the entire digital industry with categories such as connectivity (infrastructure, use, affordability), technologies (e.g. cellular M2M connections and social media penetrations), and digital solutions/use cases. The Index is meant to be a dynamic tool to be regularly updated in the coming years as new data and technologies become available.
We are conscious of the fact that the SDGs are the most ambitious development goals ever agreed globally, and that 2030 is barely a decade away. We also know that no individual stakeholder – countries, industry, civil society – can achieve them alone. That is why in our report we reiterate our commitment to work with our members and the broader digital industry to scale up the positive impact of digital, flip the negative ones, and continue to innovate for all SDGs. We also look forward to joining forces with all relevant stakeholders, policy-makers, businesses from outside the digital sector, and the SDG community, to steer the digital transformation and help deliver the Goals. Let’s make it happen!
The Global e-Sustainability Initiative (GeSI) is a strategic partnership of the Information and Communication Technology (ICT) sector committed to creating and promoting digital technologies and practices that foster economic, environmental and social sustainability. Formed in 2001, GeSI’s vision is a sustainable world through responsible, ICT-enabled transformation. GeSI fosters global and open cooperation, informs the public of its members’ voluntary actions to improve their sustainability performance, and promotes technologies that foster sustainable development. GeSI enjoys a diverse and global membership, representing around 30 of the world’s leading ICT companies and partners with over 30 global business and international organizations, as well as a range of international stakeholders committed to ICT sustainability objectives to share and develop ideas, launch joint initiatives, and collaborate on a broad range of sustainability projects. These partnerships help shape GeSI’s global vision regarding the evolution of the ICT sector, and how it can best meet the challenges of sustainable development.
For more information, see www.gesi.org.
Further details about the Enabling the Global Goals report and Digital Access Index can be found at www.digitalaccessindex-sdg.gesi.org.